Friday, August 20, 2004
Device Descriptors
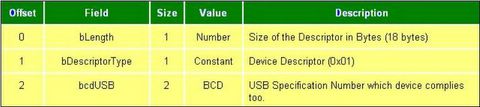
->The bcdUSB field reports the highest version of USB the device supports. The value is in binary coded decimal with a format of 0xJJMN where JJ is the major version number, M is the minor version number and N is the sub minor version number. e.g. USB 2.0 is reported as 0x0200, USB 1.1 as 0x0110 and USB 1.0 as 0x0100.
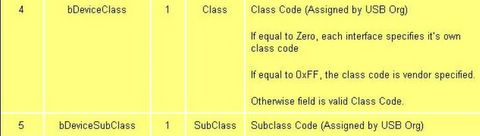
->The bDeviceClass, bDeviceSubClass and bDeviceProtocol are used by the operating system to find a class driver for your device. Typically only the bDeviceClass is set at the device level. Most class specifications choose to identify itself at the interface level and as a result set the bDeviceClass as 0x00. This allows for the one device to support multiple classes.
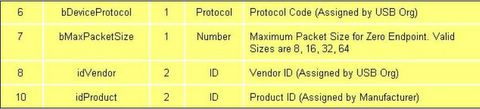
->The bMaxPacketSize field reports the maximum packet size for endpoint zero. All devices must support endpoint zero.
->The idVendor and idProduct are used by the operating system to find a driver for your device. The Vendor ID is assigned by the USB-IF.
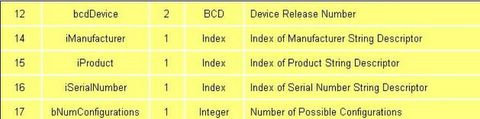
->The bcdDevice has the same format than the bcdUSB and is used to provide a device version number. This value is assigned by the developer.
->Three string descriptors exist to provide details of the manufacturer, product and serial number. There is no requirement to have string descriptors. If no string descriptor is present, a index of zero should be used.
->bNumConfigurations defines the number of configurations the device supports at its current speed.

